When is Laparoscopic GI Surgery the Right Choice for Managing Digestive Disorders
- Dr. Prashanth K

- Nov 28, 2025
- 4 min read
Digestive disorders affect millions of people worldwide, often causing discomfort, pain, and disruptions to daily life. While many conditions can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes, some cases require surgical intervention. Laparoscopic gastrointestinal (GI) surgery has become a popular option for treating various digestive disorders due to its minimally invasive nature and faster recovery times. But when exactly should patients and doctors consider this approach? This article explores the key factors that make laparoscopic GI surgery the right choice for managing digestive disorders.
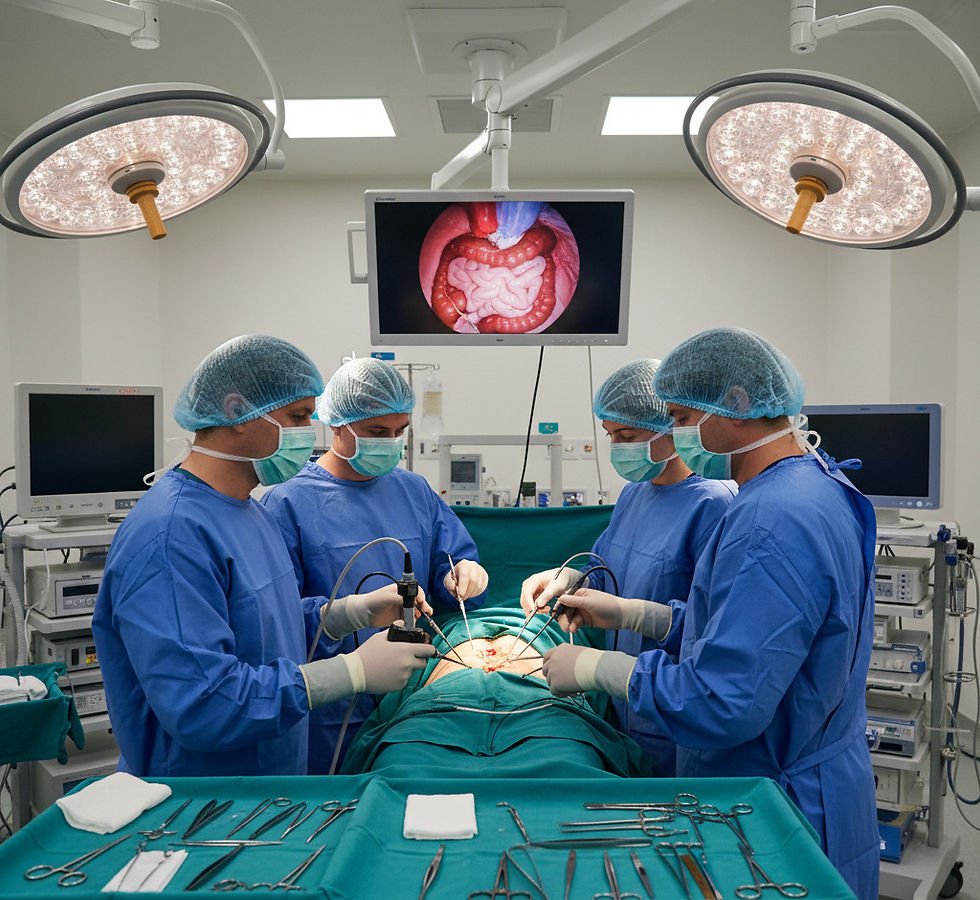
Understanding Laparoscopic GI Surgery
Laparoscopic GI surgery involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a camera and surgical instruments are inserted. The surgeon views the internal organs on a monitor and performs the procedure with precision. Compared to traditional open surgery, this technique reduces trauma to the body, lowers the risk of infection, and shortens hospital stays.
This method is used to treat a variety of digestive disorders, including gallbladder disease, appendicitis, hernias, and certain cancers. It also plays a role in managing chronic conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) when other treatments fail.
When Medication and Lifestyle Changes Are Not Enough
Many digestive disorders respond well to non-surgical treatments such as diet modification, medications, and physical therapy. However, surgery becomes necessary when these options no longer control symptoms or when complications arise.
For example, patients with gallstones causing repeated attacks or inflammation often require gallbladder removal. Similarly, individuals with severe acid reflux that damages the esophagus may benefit from laparoscopic fundoplication, a procedure that strengthens the valve between the stomach and esophagus.
In cases of chronic conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, surgery may be needed to remove damaged sections of the intestine or to address complications such as strictures or fistulas.
Key Indicators for Laparoscopic Surgery
Several factors influence the decision to proceed with laparoscopic GI surgery:
Severity of symptoms: Persistent pain, bleeding, or obstruction that affects quality of life.
Failure of conservative treatments: When medications and lifestyle changes do not improve the condition.
Presence of complications: Such as infections, perforations, or cancerous growths.
Patient’s overall health: Suitable candidates should be able to tolerate anesthesia and surgery.
Surgeon’s expertise and facility resources: Availability of skilled laparoscopic surgeons and appropriate equipment.
Patients should discuss these factors thoroughly with their healthcare provider to understand the risks and benefits.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery for Digestive Disorders
Choosing laparoscopic surgery offers several benefits over traditional open surgery:
Smaller incisions lead to less pain and scarring.
Reduced blood loss during the procedure.
Shorter hospital stays, often allowing discharge within 24 to 48 hours.
Faster return to normal activities, sometimes within a week.
Lower risk of infection and other complications.
Better visualization of internal organs through the camera, aiding precision.
These advantages make laparoscopic surgery especially appealing for patients who want to minimize downtime and recover quickly.
Examples of Digestive Disorders Treated with Laparoscopic Surgery
Here are some common digestive disorders where laparoscopic surgery is often the preferred treatment:
Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy) for gallstones or gallbladder inflammation.
Appendectomy for acute appendicitis.
Hernia repair, including hiatal hernias affecting the diaphragm.
Surgical treatment of GERD, such as fundoplication.
Resection of diseased bowel segments in Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
Removal of certain tumors in the stomach, colon, or rectum.
Each condition has specific criteria for surgery, and laparoscopic techniques continue to evolve, expanding the range of treatable disorders.
Preparing for Laparoscopic GI Surgery
Preparation is crucial for a successful outcome. Patients typically undergo preoperative evaluations including blood tests, imaging studies, and consultations with specialists. Instructions may include fasting before surgery and adjusting current medications.
Postoperative care involves pain management, wound care, and gradual reintroduction of diet and physical activity. Following the surgeon’s guidance helps reduce complications and speeds recovery.
When to Seek a Second Opinion
If surgery is recommended, patients should feel empowered to seek a second opinion, especially if the diagnosis is complex or the surgery carries significant risks. Understanding all available options, including non-surgical treatments and different surgical approaches, helps patients make informed decisions.
Final Thoughts on Choosing Laparoscopic GI Surgery
Laparoscopic GI surgery offers a less invasive option for managing many digestive disorders, especially when symptoms persist or complications develop. The decision to proceed depends on the severity of the condition, response to other treatments, and overall health.
Patients should work closely with their healthcare team to evaluate the benefits and risks. When chosen appropriately, laparoscopic surgery can improve quality of life, reduce recovery time, and provide effective relief from digestive disorders.
If you or a loved one struggles with a digestive condition that does not respond to medication or lifestyle changes, consult a specialist to explore whether laparoscopic GI surgery is the right next step.



Comments